
(PDF) I. INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS on MEDICINAL and AROMATIC PLANTS
Huckel's Rule is a set of algorithms that combine the number of π π electrons ( N N) and the physical structure of the ring system to determine whether the molecule is aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. The number of π π electrons in an aromatic system can be determined by the following algorithm: N = 4n + 2 (17.5.1) (17.5.1) N = 4 n + 2.
Synthesis of Aromatic Compounds
Constructing Molecular Orbitals • molecular orbitals are the sideways overlap of porbitals •porbitals have 2 lobes.Plus (+) and minus (-) indicate the opposite phases of the wave function, not electrical charge •When lobes overlap constructively, (+ and +, or - and -) a bonding MO is formed

aromatic1.pdf Aromaticity Ion
This rule would come to be known as Hückel's Rule. Criteria for Aromaticity 1) The molecule is cyclic (a ring of atoms) 2) The molecule is planar (all atoms in the molecule lie in the same plane).

(Download) "Aromaticity in Heterocyclic Compounds" by Tadeusz Marek
According to Hückel's Molecular Orbital Theory, a compound is particularly stable if all of its bonding molecular orbitals are filled with paired electrons.This is true of aromatic compounds, meaning they are quite stable. With aromatic compounds, 2 electrons fill the lowest energy molecular orbital, and 4 electrons fill each subsequent energy level (the number of subsequent energy levels is.

Aromaticity PDF
Aromaticity. Page ID. William Reusch. Michigan State University. The adjective "aromatic" is used by organic chemists in a rather different way than it is normally applied. It has its origin in the observation that certain natural substances, such as cinnamon bark, wintergreen leaves, vanilla beans and anise seeds, contained fragrant compounds.
Full article Overview of Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds (PAC)
uninterrupted cyclic cloud of π electrons above and below the plain of the ring. The German. Chemist Erich Hückel was the first one to recognize that an aromatic compound must have an odd number of pairs of electrons, which can mathematically be written as 4n+2 (n = 0,1,2,3 etc).

buy book Aromatic & Essential Oil Plants 9789383284092
Aromaticity is one of the most deeply rooted concepts in chemistry. But why, if two-thirds of existing compounds can be classified as aromatic, is there no consensus on what aromaticity is? σ−, π−, δ−, spherical, Möbius, or all-metal aromaticity… why are so many attributes needed to specify a property? Is ar 2023 Chemical Science Perspective & Review Collection Emerging.

Aromatic Compounds.pdf Aromaticity Pyridine
20364 Altmetric 13 Citations 653 LEARN ABOUT THESE METRICS Export RIS PDF (30 KB) Get e-Alerts SUBJECTS: Aromatic compounds, Aromaticity, Electrical energy, Energy, Hydrocarbons Michael Faraday discovered benzene in 1825 ( Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London, 1825, 440).

Answer Aromaticity 09 PDF PDF
Aromatic Dianions I 1H NMR: d6.75, singlet Cyclooctatetraene anti-aromatic tub-shaped Cyclooctatetraenyl anion aromatic planar 1H NMR: d5.56, singlet 2 Na = Aromatic Dianions II Dihydropentalene H 2 n-butyllithium H H H Pentalene dianion Pentalene. The End. Created Date:

(PDF) Aromaticity Concepts Derived from Experiments
Aromaticity and Antiaromaticity A comprehensive review of the science of aromaticity, as well as its evolution, from benzene to atomic clusters In Aromaticity and Antiaromaticity: Concepts and Applications, a team of accomplished chemists delivers a comprehensive exploration of the evolution and critical aspects of aromaticity.

Aromatic Chemistry Textbook
Pages 1 - 41 Abstract In this chapter, the main aspects that govern the relationship between aromaticity (as well as antiaromaticity) and molecular orbitals (MOs) are presented and discussed. The Hückel and Möbius theories are discussed first.

Reference Book Maria Mitchell Herbalist
Aromaticity is a property of conjugated cycloalkenes in which the stabilization of the molecule is enhanced due to the ability of the electrons in the π π orbitals to delocalize. This act as a framework to create a planar molecule. Introduction Why do we care if a compound is aromatic or not?
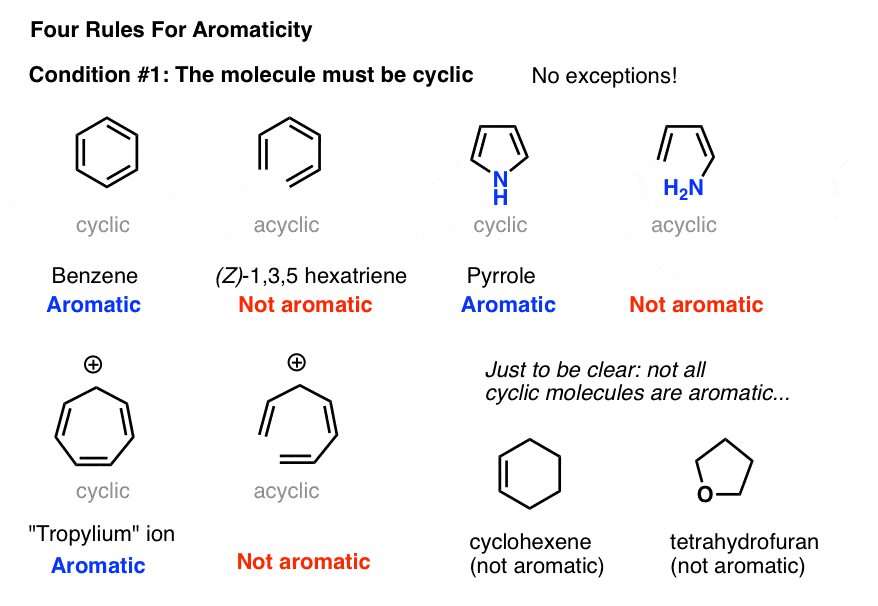
Rules for Aromaticity The 4 Key Factors Master Organic Chemistry
TrimSize:8inx10in Klein5e-Vol2 c01.tex V1-September13,2019 5:12P.M. Page3 1.2 NOMENCLATURE OF AROMATIC COMPOUNDS 3 CH 3 Toluene OH Phenol

Aromaticity 1st Edition
Aromaticity and Antiaromaticity A comprehensive review of the science of aromaticity, as well as its evolution, from benzene to atomic clusters In Aromaticity and Antiaromaticity: Concepts and Applications, a team of accomplished chemists delivers a comprehensive exploration of the evolution and critical aspects of aromaticity. The book examines the new global criteria used to evaluate.
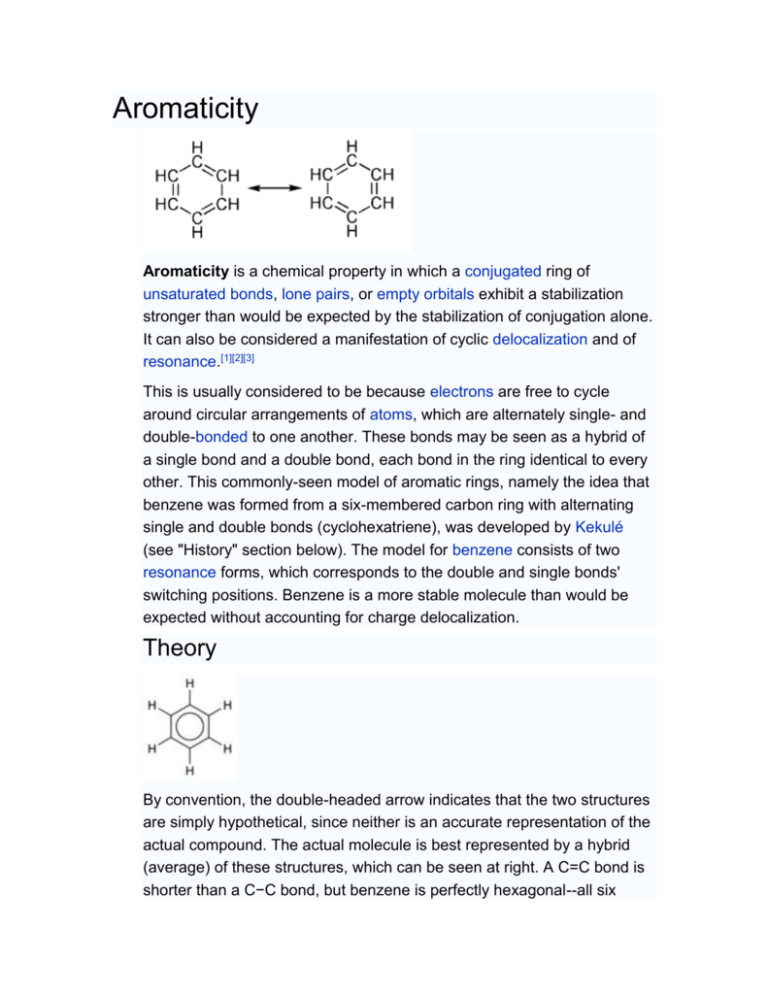
Aromaticity
Benzenoid aromatic compounds are the organic molecular species either with isolated benzene rings or with multiple benzene rings which fused to form a more complex structure. Therefore, these compounds can further be classified into monocyclic aromatic compounds and polycyclic aromatic compounds. Monocyclic aromatic compounds: Polycyclic.

(PDF) Manual of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants
Aromaticity and Antiaromaticity | Wiley Online Books Aromaticity and Antiaromaticity: Concepts and Applications Author (s): Miquel Solà, Alexander I. Boldyrev, Michał K. Cyrański, Tadeusz M. Krygowski, Gabriel Merino First published: 14 October 2022 Print ISBN: 9781119085898 | Online ISBN: 9781119085928 | DOI: 10.1002/9781119085928